We has produced various forms of grid , and the precision machining of the components ensures a tight fit.
The trial assembly is a standard control process, and a test report is issued to ensure it exactly meets the as-built dimensions.
Application: Gas sweetening, gas drying, sulphur removal, hydrotreating, hydrocracking, hydrogenation, etc.
Design based on your application
The catalyst is selected for its efficiency, stability, and selectivity. The required catalyst volume forms a bed with a fixed height based on the reactor's diameter.
A catalyst loading diagram outlines the sequence of inert balls and various catalyst types, each with specific sizes and bulk densities. These catalyst layers can form a single bed or multiple beds in a multi-bed reactor, requiring the installation of multiple support grids within the same reactor.
In axial flow operations, the support grid assembly must endure vertical process loads. To ensure strength, the grids are reinforced or supported by additional beams. Several configuration examples are provided.
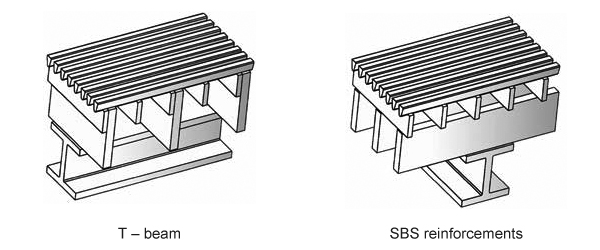
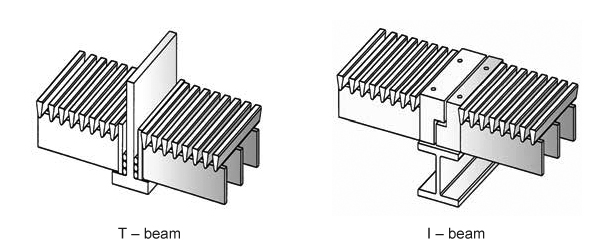
T-shaped and I-shaped beams are commonly used. T-beams are typically selected for high design pressures, as they allow a significant portion of the web to be embedded within the bed above the grid. In contrast, I-beams are more suited for lighter design pressures, positioning the beam below the grid.
The support grid is mounted on a ring that is integral to the pressure shell. It is constructed in sectors for installation through the vessel manhole. Certain processes require a locking system to secure the panels in place.
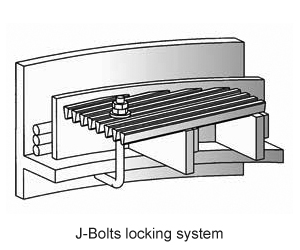
A small gap is maintained between the support grid and the vessel wall to accommodate differential thermal expansion, provide installation clearance, and account for manufacturing tolerances or any out-of-roundness of the reactor.

Rope packing for catalyst sealing
Design Parameters
Process parameters:
Key process parameters include design and operating temperature, pressure drop through the catalyst, opening size, and percentage of open area. Additional conditions, such as changes in flow direction and process cycles, are needed to determine the appropriate grid assembly type.
Mechanical parameters:
Mechanical requirements, such as manhole size, catalyst weight, and corrosion allowance, are essential for defining the necessary reinforcement, if any.