-
Application of Continuous Flow Reactors in High-Risk Processes
2025-09-22
According to the State Council's Work Safety Committee, high-risk chemical processes include nitrati
-
Significant Advantages of Microreactors Over Conventional Tank Reactors
2025-07-23
Microreactors have significant advantages over conventional tank reactors. They can precisely contro
-
2025-07-07
Nitrification is the process of introducing nitro groups to organic molecules and has wide applicati
-
22 2025-09
Application of Continuous Flow Reactors in High-Risk Processes
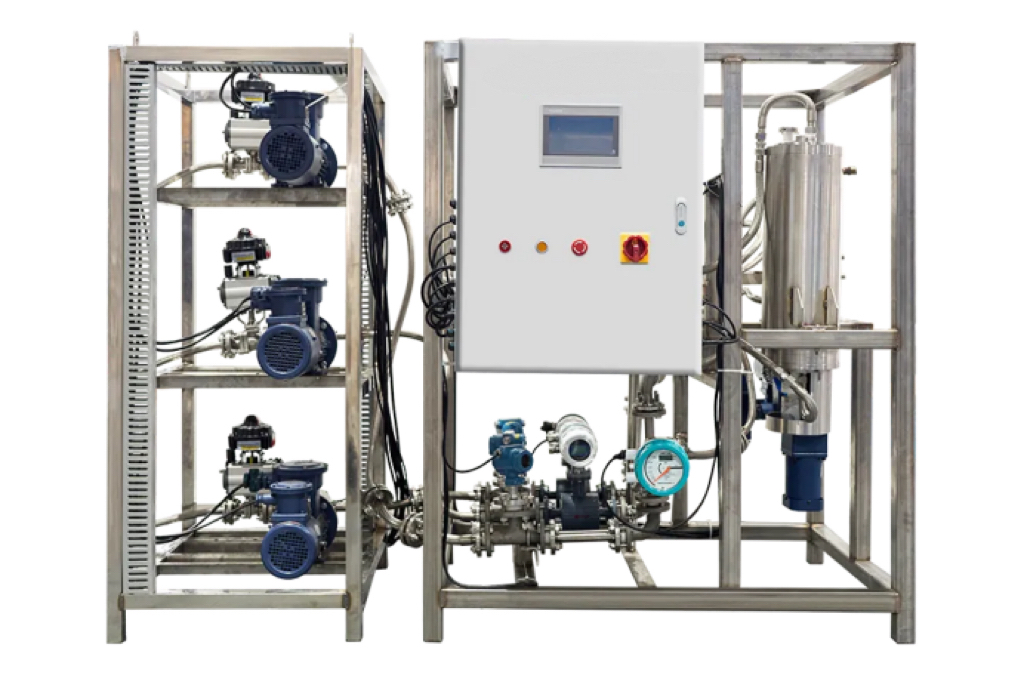
According to the State Council's Work Safety Committee, high-risk chemical processes include nitration, chlorination, fluorination, ammoniation, sulfonation, hydrogenation, diazotization, oxidation, peroxide treatment, cracking, and polymerization. These processes pose significant risks such as toxic gas leaks and high-pressure explosions. Continuous flow reactors, as advanced technology, offer improvements in safety and yield compared to traditional reactors. This article analyzes the suitability of continuous flow reactors for hazardous processes like phosgene reactions, which involve highly toxic gas risks, combustion and explosion hazards, and corrosive byproducts like hydrochloric acid. The goal is to enhance safety in chemical production and reduce fear associated with these processes.
-
23 2025-07
Significant Advantages of Microreactors Over Conventional Tank Reactors
Microreactors have significant advantages over conventional tank reactors. They can precisely control reaction temperature, dissipating heat in time during strong exothermic reactions to avoid local overheating and by - product generation. They also precisely control reaction time through continuous flow reactions in microtubing, preventing excessive by - products due to long reaction times. Materials can be mixed evenly in an instant with precise proportions in microreactors, reducing by - product formation for rapid reactions with strict material ratios. Microreactors are safer as they use continuous flow reactions, keeping the amount of chemicals in the reactor low and limiting potential harm. Their excellent heat transfer efficiency also ensures stable reaction temperatures. Moreover, microreactors have no amplification effect. Process scale - up is achieved by increasing the number of microchannels, allowing direct application of small - test optimal reaction conditions to production and shortening the product development cycle.
-
07 2025-07
Nitrification is the process of introducing nitro groups to organic molecules and has wide applications in the chemical industry, especially in explosives and energetic materials manufacturing. The introduction of nitro into aromatic rings and heterocycles serves three main purposes: converting nitro to other substituents, activating other groups on the aromatic ring, and giving fine - chemical products specific properties. The nitrification process has two types: batch and continuous. The batch process has production risks due to post - reaction raw material reactions, while the continuous process improves efficiency and reduces labor intensity but has a low industry application proportion. Some companies stick to the batch process for flexible adjustment according to market changes, and many lack awareness of nitrification hazards. Local governments have introduced strict policies to ensure safety. Micro - chemical technology, represented by the microchannel reactor, is a new environmentally friendly chemical technology. It offers effective solutions for nitrification reactions with its small area, reasonable resource utilization, and low energy consumption. Examples show its high efficiency, safety, and product selectivity in nitrification reactions. In conclusion, the continuous flow reactor has significant advantages in the dangerous nitrification process, achieving intrinsic safety and revolutionizing chemical production.
-
30 2025-06
The Difference Between Internal Reflux and External Reflux in the Distillation Column
In a distillation column, internal reflux is the downward - flowing liquid from the top, formed by a pump at the bottom drawing overhead liquid and re - injecting it. It can reduce top - column concentration, improve distillation liquid efficiency and product quality, but it increases equipment cost and maintenance expenses, and improper control may cause negative effects. External reflux is the upward - flowing liquid from the bottom, achieved by a separator or level regulator. It can improve separation efficiency and save equipment and maintenance costs, yet it increases the liquid's bubble point, may reduce distillation efficiency, and excessive reflux can cause problems. Both internal and external reflux have pros and cons, and the choice depends on specific operational needs; for demanding distillation, a combination of the two is often used for optimal separation.

3153-3 Lvxiang Village, Jinshan District, Shanghai
No.1, Sanqiang Road, Rugao City, Jiangsu
Tel: +86 13651755429;+86 13916961821
Email: ys.zhu@ekaislot.com;zsy@ekaislot.com
Contact Now